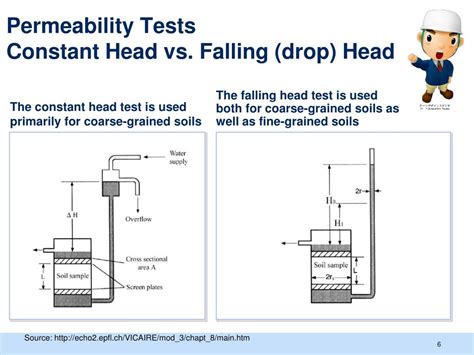
variable head permeability test pdf|falling head permeability test astm : custom Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test .
Canais da Globo dominam 'pódio' da TV paga com Copa do .
{plog:ftitle_list}
16 de jan. de 2024 · Assistir Online Terra e Paixão Capítulo 213 de 10/01/2024 completo em HD. Mais recente transmita Grátis online ou baixe Terra e Paixão Capítulo 213 no NovelasFlix. Não se esqueça de curtir e compartilhar este vídeo, marque também este site para ficar por dentro dos vídeos diários do Terra e Paixão AO VIVO. Read More ».
falling head vs constant permeability
Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to .1 INTRODUCTION. In situ permeability tests performed in wells and in casings .
Constant head tests are most often carried out as inflow tests (where water is added to the borehole), but outflow tests (where water is pumped out of the borehole) can also be carried out. The equipment required is rather more .
friction testing services
The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable .One is constant head permeability test And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval.Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test .permeability of soil governs the type of soil to be used. 0.4 This Standard ( Part 17) covers both constant head and falling head tests as used for most of the soil. The laboratory determination .
Interpreting in Situ Variable-Head Permeability Tests - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Variable-head permeability tests can be performed in open boreholes or monitoring wells having either a long screen or several screened zones. In all cases, a test .
1 INTRODUCTION. In situ permeability tests performed in wells and in casings during drilling are a very common tool to determine the local hydraulic conductivity K of an aquifer. Two methods.tion of coefficient of permeability of soils using falling head and the constant head methods. This test is recommended for soils with coefficient of permeability in the range lo- 3 to 10-v cm/s and maximum particle size of 9.5 mm. 2. TERMINOLOGY 2.1 For the purpose of this standard, definition terms given in
- The permeability of soils is also required in design of filter used to prevent piping in hydraulic structures. STANDARD LABORATORY TESTS Two standard laboratory tests are used to determine the coefficient of permeability of soil: I- CONSTANT HEAD TEST In the constant head test, water is made to flow through a column of soil underD 4254 Test Methods for Minimum Index Density of Soils and Calculation of Relative Density3 3. Fundamental Test Conditions 3.1 The following ideal test conditions are prerequisites for the laminar flow of water through granular soils under constant-head conditions: 3.1.1 Continuity of flow with no soil volume change during a test,There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s).The document describes procedures for conducting a falling head permeability test to determine the coefficient of permeability (k) of soils. The test involves measuring the change in water height over time as water flows through a soil sample confined in a standpipe. The k value is then calculated using an equation that relates the height changes, sample dimensions, and elapsed .
Variable head permeability tests are routinely executed during exploratory drilling and they are very popular due to their low cost. Sealing of the testing tip is ensured by the convergence of the .The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1.
Constant Head Permeability Test The constant head permeability test is a laboratory experiment conducted to determine the permeability of soil. The soils that are suitable for this tests are sand and gravels. Soils with silt content cannot be tested with this method.The test can be employed to test granular soils either reconstituted or disturbed.
D 4254 Test Methods for Minimum Index Density of Soils and Calculation of Relative Density3 3. Fundamental Test Conditions 3.1 The following ideal test conditions are prerequisites for the laminar flow of water through granular soils under constant-head conditions: 3.1.1 Continuity of flow with no soil volume change during a test,
Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests .FALLING HEAD TEST It also called variable-head test. For relatively less permeable soils, the quantity of water collected in the graduated cylinder of the constant-head permeability test is very small and cannot be measured accurately. For such soils, the falling head permeability test is used. APPARATUS 1- Permeameter device as shown in figure . Now a falling or constant head permeability test may be conducted, depending on the type of soil. The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 . PDF | Trapped gas and cavity expansion may affect the data of a variable-head test in a monitoring well. In a low- permeability material, some gas may. | Find, read and cite all the research you .
🕑 Reading time: 1 minute Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow water to flow its pores or voids. Permeability is one [.] The two well established methods in engineering practice are the constant head permeability test and the falling head permeability test- Klute (1986), Dirksen (1999), Das (2002), Reynolds et al . Variable Head Permeability Tests in Monitoring Wells: Comparing the Shape Factor Defined by Bouwer and Rice (1976) to the Shape Factor Given by Hvorslev (1951) Geotechnical News 27
permeability and specifically to test the aquifer. They are not able to accurately measure soil permeability in areas of low permeability, such as the existing soil in its existing condition from the ground surface down to the aquifer. Once the proposal for the permeability testing methodology has been reviewed and approved, it is The performance of clayey liners and covers is assessed by several methods including borehole variable-head permeability (k) tests. Different interpretations of the end-of-casing and Lefranc tests are discussed. In Quebec, most tests have been interpreted using the velocity-graph method. Its equations are presented and differences are illustrated by .
It is a valid test for soils with a high rate of flow like sands and gravels, but also some clay soils. Falling Head Test allows the head to decrease as water infiltrates the sample, diminishing the pressure over the course of the test. Falling head methods are generally limited to fine-grained soils. Soil Permeability Testing EquipmentOpen PDF. Géotechnique. ISSN 0016-8505 | E-ISSN 1751-7656. Volume 55 Issue 9, November 2005, . Non-steady flow in the variable-head permeability test Authors: J. J. Nader * x. J. J. Nader. Search for articles by this author * Department of Structural and Foundation Engineering, Polytechnic School, University of São Paulo. Brazil. Author .
Constant Head Permeability Test. 2. Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability Test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is suitable for coarse grained soils which are relatively more pervious because of their larger voids. While variable head is more suitable .The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods:
Interpreting in Situ Variable-Head Permeability Tests - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
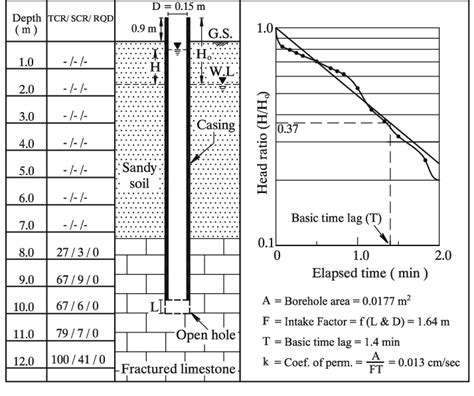
FALLING/VARIABLE HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST (ASTM D5084) • Mainly used for fine-grained soils but can also be used for coarse-grained soils. • Procedure is same as constant head test except: • Record initial head difference, h 1 at t=0. • Allow water to flow through the soil specimen. • Record the final head difference, h 2 at t=t 2.Two types of variable-head permeability tests in driven flush-joint casings, the end-of-casing test and the lateral injection test (Lefranc test), were performed in two sand tanks. Hydraulic conditions in the sand tanks included a constant vertical hydraulic gradient that was null, positive, or negative. The gradients were monitored by lateral piezometers, which confirmed that the .Where, K27 = Permeability at 27°C KT = Permeability at T°C μ27 = Coefficient of Viscosity at 27°C μT = Coefficient of Viscosity at T°C. 5.5 Presentation of Results: The values of permeability at T 0 C and 27 0 C are reported. Also reported are corresponding void ration, degree of saturation and water content. 6. Falling Head Test Field permeability from falling head test versus depths compared to pumping test results. . Estimation of soil permeability.pdf. . meability is highly variable within the same deposit with a.
friction tests
webBaixar documentos O que são os Documentos Top? O que eu preciso para baixar um documento? Onde eu encontro os meus documentos baixados? Gostaria de baixar um documento mas não consigo ver a pré-visualização. O que posso fazer? Se eu não estiver satisfeito com a qualidade do documento?
variable head permeability test pdf|falling head permeability test astm